How Much Do I Need to Buy a Home?
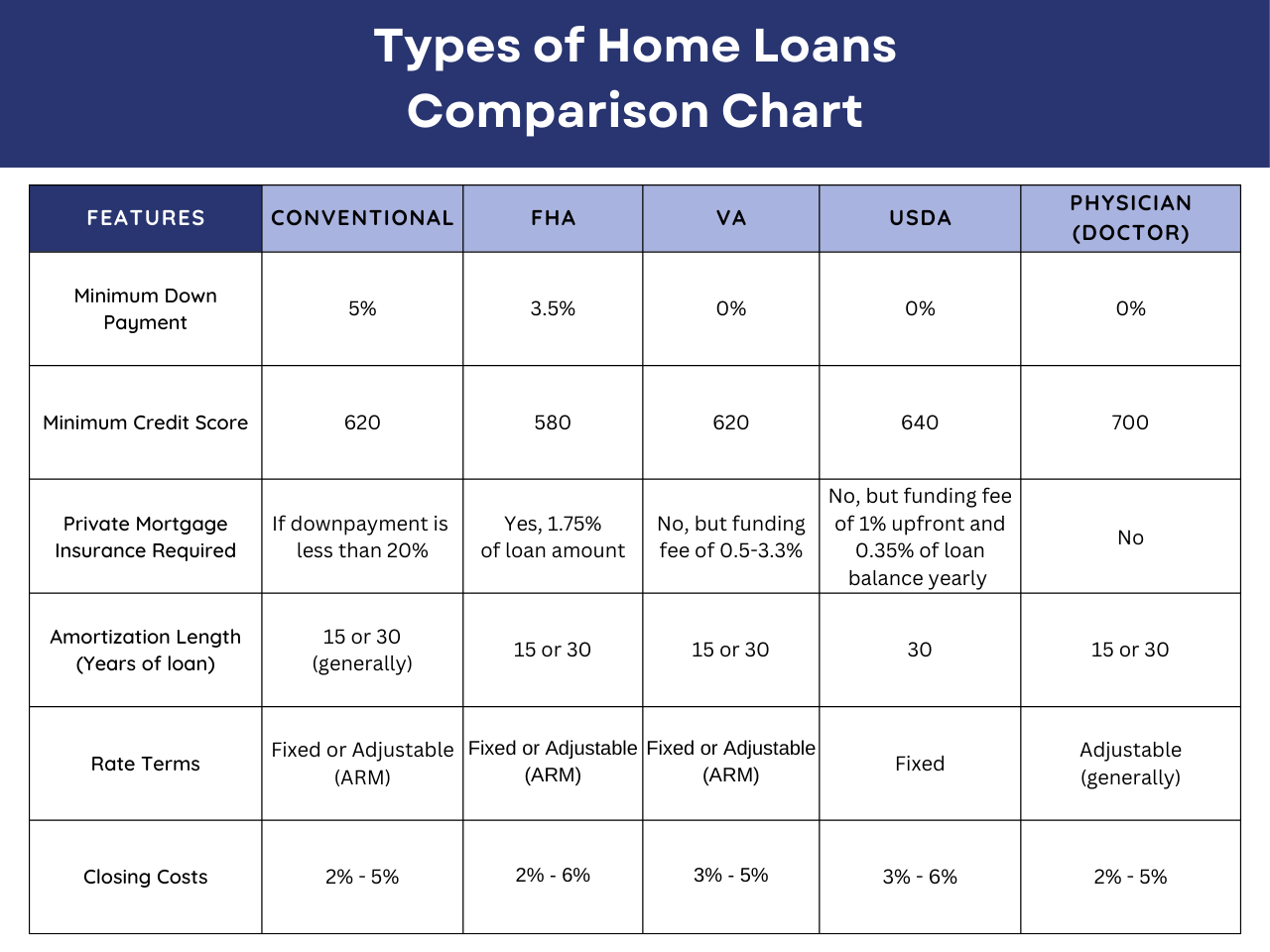
Loan Options
Getting into the housing market means balancing upfront costs with your financial goals. Here’s an overview of what you’ll need and how different loan options affect the cost.
Understanding Down Payments
Conventional Loans: Typically require 5-20% down, though some lenders allow as little as 3%.
FHA Loans: Government-backed loans with down payments as low as 3.5%.
VA Loans: Available for veterans and active-duty military, requiring no down payment.
USDA Loans: Zero down for eligible rural and suburban properties.
Physician Loans: Designed for physicians and dentists, these loans allow for no down payment without private mortgage insurance (PMI), and typically do not include student loans into the debt to income ratio.
Closing Costs & Reserves
Typically, closing costs range from 2-5% of the home price, covering fees like title insurance, appraisal, and lender fees. Most lenders may require additional reserves—money in the bank—to ensure you have funds beyond the down payment. You will most likely be required to pay 12-15 months of homeowners insurance and 6 months of property taxes (these are included in the 2-5% estimate).
Inspections
A home inspection is an essential step in protecting your investment, even for newly built homes under warranty. Home inspection fees typically range from $750 to $1,200, based on the types of inspections required, which often include:
Whole Home Inspection: An extensive check from roof to foundation, potentially recommending licensed specialists for specific areas like HVAC, electrical, or structural.
Wood Destroying Insects: Termite inspections are usually required by lenders and can reveal issues with pests like termites, carpenter bees, or wood-boring beetles.
Radon Testing: Radon, a natural gas linked to lung cancer, is commonly tested in areas with known high levels, such as central Kentucky.
Septic System Check: Ensures any septic system is functioning as intended, preventing future costly repairs.
Comprehensive inspections help uncover potential issues early, offering peace of mind and safeguarding your investment.
Other Considerations
Private Mortgage Insurance: Required for loans with less than 20% down but is often waived for VA and physician loans. This is not the same as homeowner’s insurance that protects the home and your contents.
Origination Fees: Mortgage origination fees are one-time charges from the lender for processing a loan, typically covering administrative costs, underwriting, and document preparation. These fees are usually calculated as a percentage of the total loan amount and can vary based on the lender, loan type, and borrower’s credit profile.
Understand Fees and How to Compare Them
Comparing loan estimates from at least three lenders can help secure the best rates and terms. Some lenders may offer a better rate, but build in upfront costs that ultimately make the loan more expensive.
By understanding these options and saving for your specific needs, you can better prepare for the home-buying journey, choosing the best loan structure to support your financial future.